PUBLISHING DESIGN | EXERCISES
08/04/19 - 29/04/19 | Week 2 - Week 5
Yeoh Xiao Shi (0331577)
Publishing Design
Exercises
LECTURE
Lecture 1 : Formats
08/04/19 (Week 2)
This week, we were given a lecture about the book formats since this module will be centered around the book. Through the lecture, we got to look into few different formats used across time in different civilizations around the world which includes Mesopotamian civilization, Ancient Egyptian civilization, Indus Valley civilization, Han Chinese civilization and European civilization.
01. Mesopotamian Civilization
• first writing system developed from a counting technology
• the progression from simple and complex tokens to bullae set
• pictographic writing on clay tablets
02. Indus Valley Civilization
• their writing, cuneiform was one of the earliest systems of writing
• writing on soft clay tablets by using sharp pointed tools
03. Ancient Egyptian Civilization
• scribes were the only people in ancient Egypt that could read and write Hieroglyphics
• write on papyrus and tomb wall
04. Han Chinese Civilization
• Chinese characters in the early period are written in vertical columns on a thin strip of bamboo
• earliest known printed book is Chinese, from the end of Tang dynasty
• use scroll format for their book
• pioneer of movable type but has been achieved in Korea
05. European Civilization
• invented parchment with animal hide
• started to make parchment book around 50 AD
Embedded PDF of week 2 lecture slides.
Lecture 2 : History of Print
15/04/19 (Week 3)
This week, Mr Vinod started off the class by giving us a lecture about the history of print. Throughout the lecture given, we are able to learn different printing methods used in the past and the discovery of the printing across different countries back in the day till now.
To sum up,
• paper was first invented in China and it is probably one of the most important ingredients in the process of printing
• transfer was initially done by rubbing the stone to the paper surface, hence mass production was enabled
• the earliest printed document was in Korea while the first printed book is in Chinese
• movable type was pioneered in China but achieved in Korea
• the world's largest book is set in stone and it is located in Mandalay, Myanmar
Embedded PDF of week 3 lecture slides.
Lecture 3 : The Grid
22/04/19 (Week 4)
In this class, we were given a lecture about the grid which is one of the important system used by designers for solving visual problems in two or three-dimensions. It is said to be important for the designer to arrange the elements like texts, photographs and diagrams in the form of a grid in resulting the coherent and functional visual. This creates a sense of compact planning, intelligibility and clarity as well as suggests orderliness in design.
There is a scientifically proved fact about the information that is presented in clear and logically set out titles, subtitles, texts, illustrations and captions will be retained and understood better. Thereore, our responsibilty as designers are towards those who are going to experience and use or interact with our works. We have to put ourselves in the reader's perspective in order to come up a design that can make the user experience seamless and engage them when reading our book.
Embedded PDF of week 4 lecture slides.
Lecture 4 : Typography Redux
29/04/19 (Week 5)
This week, Mr Vinod began the class by giving us a lecture about Typography which is the most important area in graphic design to master. Through this lecture, we are able to revise what we have learned in the previous semester.
Typography is the art of arranging and composing text, it is also a medium for expression and most importantly communication. It plays a centrol role in any design work. If the goal when working with type is to make a body text more readable, then heeding established legiblity guidelines is of utmost importance. Departure rom these "rules" should be attempted when the designer is totally familiarized with them, and when the content lends to expressive interpretation. As to achieve legibility, we need to choose text typefaces that are open and well propotional. For example, classical serif typefaces like Garamond, Bodoni, Minion Pro, Baskerville, Jenson, Caslon and the sans serif typefaces like Franlin Gothic, Frutiger, Gill Sans, Helvetica, Myriad Pro and more. Other than choosing the right typeface, they are also other aspects that we need to consider like special styles, type size, line length, line spacing, character, word space, alignment, paragrah indent and special formatting.
Embedded PDF of week 5 lecture slides.
INSTRUCTIONS
EXERCISES
Week 2 (08/04/19)
For the first exercise, we were instructed to explore three possible sizes for the book that we are going to create in project 1. The size requirement for the book is that it should be bigger than A5 but smaller than A4. Once we figured out the sizes, we were told to outline the one that we prefer more with a different color pen. For me, I decided to go with the size of 180mm x 220mm.
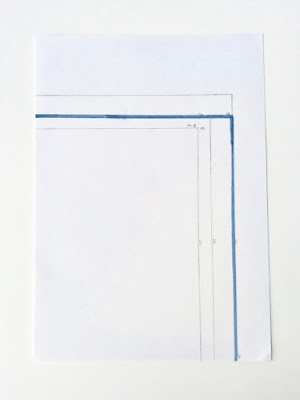 |
| Fig.1.1: Size Exploration. |
After finalizing the size, we were then tasked to create a mock-up book with 8 pieces of A3 paper. To start off, we were told to fold the papers into half and staple binding them. Then, we proceeded to cut the book to size. Throughout the process, I manage to learn the right way to bind the booklet as well as cutting the huge amount of paper at the same time.
 |
| Fig.1.2: Completed mock-up. |
 |
| Fig.1.3: Staple binding. |
 |
| Fig.1.4: Spread. |
Classical Grid Structure
Week 3 (15/04/19)
In today's class, we were required to construct the grid which
As I drew some angles of the lines wrongly, the height of the text area were not proportional in both sides. Therefore, I try to make a second attempt after the class.
 |
| Fig.2.1: Van de Graaf grid. (first attempt) |
 |
| Fig.2.2: Van de Graff grid. (second attempt) |
After constructing the grid on paper, we were tasked to do it digitally in Adobe InDesign. The process of digitizing is considered much easier for me since I could create a better straight line in Adobe InDesign.
 |
| Fig.2.3: Process of constructing the grid in Adobe InDesign. |
 |
| Fig.2.4: Digitized grid based on the chosen size of the book. |
Signature Folding Systems (Week 3)
Week 3 (15/04/19)
In the same class, we were given another exercise which we need to fold an A3 paper into 8 equal pages and then number each page accordingly from 1-16 as there are 16 pages in one signature.
 |
| Fig.2.5: Signature fold. |
 |
| Fig.2.6: Signatured fold. |
 |
| Fig.2.7: Signatured fold. |
Grid System (Week 4)
Week 4 (22/04/19)
In the previous class, we were instructed to photocopy 5 spreads from a book with nice layout and bring in to this class. To start off, we were told to exhange 3 spreads with our friends and then determine the margin and column of the spreads by using grid system.
 |
| Fig.3.1: Grid structure. |
 |
| Fig.3.2: Grid structure. |
 |
| Fig.3.3: Grid structure. |
 |
| Fig.3.4: Grid structure. |
 |
| Fig.3.5: Grid structure. |
 |
| Fig.3.6: Grid structure. |
Form & Movement (Week 4 - Week 5)
Week 4 (22/04/19)
Moving on from that, we proceed to form and movement exercise. For this exercise, we were asked to explore the form in different spreads as to form a movement of the layout. It is said to be helpful for us in creating the layout of our book in the next project.
 |
| Fig.3.7: Process of exploring the form in Adobe InDesign. |
 |
| Fig.3.8: Process of exploring the form in Adobe InDesign. |
 |
| Fig.3.9: Form and movement. (B&Wstatic) |
 |
| Fig.3.10: Form and movement. (B&W animated) |
 |
| Fig.3.11: Form and movement. (One colour static) |
 |
| Fig.3.12: Form and movement. (One colour animated) |
Week 5 (29/04/19)
In the previous week, we were told to explore the form in one colour. While in this week class, we were required to explore it in two colours.
Type Formatting (Week 5)
Week 5 (29/04/19)
Week 5 (29/04/19)
For this exercise, we were required tried out few variations of typeface in order to determine the one that suits the visual style of our book.
Embedded PDF of text formatting.
FEEDBACK
Week 2
General Feedback :
Specific Feedback :
Week 3
General Feedback :
Specific Feedback :
Week 4
General Feedback : When exporting the form and movement exercise as JPEG, we were told to export it in 72 dpi so that the file won't crash.
Specific Feedback : For the exercise, I was told that some of my attempts are interesting but some look like there is too much shapes in one page so I would need to make some changes. While for my project 1, the illustrations were great so I just need to move on for what I'm doing.
Week 5
General Feedback : We were told to update our blog for exercise and project 1 as it is due in the next class.
Specific Feddback : For my visuals, overall is good and no problem. As for the exercise, I was told that I did a good job as the result seems interesting even though there are lots of elements.
REFLECTION
Experiences
Week 2 : This week, I got to experience with different manual works like exploring different book sizes, staple binding and create a book mock-up which I think is fun and interesting. However, I'm not a skillful person when it comes to measuring and cutting. Therefore, it took me more time to complete the exercise as compared to others.
Week 3 : In this class, I manage to learn something new which is to find the margin of the book by constructing the Van de Graaf grid. In addition, I also got to learn and understand about the signature book binding through the exercise given.
Week 4 : This week, I got to learn about how the grid system build and identify the margin and column through the exercise given. Also, I got to explore with the movement of the layout by playing around with the form.
Week 5 : Last week, I have experienced in creating the movement for the layout in one colour. As for this week, I got to explore it again by using two colours. At the same time, I also got to explore with various combination of typefaces in order to find out the best one for my book.
Observations :
Week 2 : I realized cutting a huge amount of paper at the same time isn't that hard if I do it in a right way. Also, I noticed it is important for us to pay full concentration while cutting the papers so that accidents could be avoided.
Week 3 : I observed it is important to make sure all the diagonal lines drawn is at the same angle.
Week 4 : I realised it is hard for me figure out the margin and column of some spreads as I get confused with the layout.
Week 5 : I noticed that the elements look more interesting after adding a secondary colour and I also realised it took up more time for me to complete this exercise as compared to last week because I focus too much on the colours. While typesetting, I realised I tend to combine the typefaces that I like and keep forgetting about my visual style. Hence, I need to remind myself to look back at my visuals and choose the typefaces.
Findings :
Week 2 : Through today's exercises, I'm able to learn about the cutting skills as well as the proper way to bind the book.
Week 3 : To have the same proportions of margin, I found that it is important to make sure all the diagonal lines drawn is at the same angle. Other than that, I manage to learn about the signature book binding which the pages of the book are printed on large sheets of paper with multiple pages printed on each side and each signature will consist 16 pages.
Week 4 : I found this two exercise that we completed in today's class are useful for us to have a better understanding on grid system as well as layout. Moreover, I think it is helpful for me in preparing for the upcoming project which is to create the layout for my book.
Week 5 : While using colours to place the form, I found that I would focus more on colours than form. Therefore, I need make it in black and white first before adding colour to it. On the other hand, I found that typesetting is an important progress for me to determine the typeface that suit the visual style of my book.
FURTHER READING (WEEK2-5)
Week 2
 |
| Publication Design By: Poppy Evans |
From this book, I got to read about the ways to apply color in publication design and production effectively. According to the author, color is a language that is universally understood. We can somehow predict that people will respond in a consistent way when they see a certain color or color combination. However, some colors have unilateral meaning, other colors and color combinations have social or cultural connotation which means the emotional reaction of a viewer to a color or color combination can sometimes depend on the meaning of that particular color has within that individual's culture. Hence, as a designer, it is important for us to understand all these differences and to select the right color for a publication design that can communicate the mood or attitude to the audience. As to determine the colors for certain publication's mood, designers would choose a color palette. From here, a color palette for a design may include various single colors or hue which is known as a monochromatic color scheme. Although it is good in supporting a design communication goal, but sometimes a combination of colors are said to be more effective. Hence, to combine the colors well, it is necessary to know about the wheel and color theory as they will guide us to determine which combinations will work together in the design.
Week 3
 |
| The Layout Book By: Gavin Ambrose & Paul Harris |
This week, I have read about the vocabulary of layout design which is basically about the design principles that can be applied in book design. Through this, the designer can visually articulate ideas and concepts that can be extremely subtle or complex.
The vocabulary includes
 |
| Vocabulary of layout design. |
01. Proximity
•
•
02. Unity
•
•
•
03. Alignment
•
•
•
04. Contrast
•
•
05. Hierarchy
•
•
06. Balance and tension
•
•
07. Juxtaposition
•
•
08. Consistency or repetition
•
09. White space
•
•
•
Week 4 - Week 5
 |
| Design th!nking By: Gavin Ambrose & Paul Harris |
(Week 4)
This week, I have read about thinking in shapes from this book. According to the authors, design elements like text blocks form approximate shapes on a page. Thus, thinking in shapes would help the designer to address general spatial relationships between the elements and how they fill the page. In 1923, Wassily Kandinsky proposed a universal relationship between the three basic shapes (triangle, square and circle) and the three primary colours (yellow, red, blue). He believed that the yellow triangle to be the most active and dynamic as well as the cold and passive blue circle to be the least so. It is said that design can be infused with different shapes to produce different tension on the page (different active and passive areas). This will lead the eye to different areas of a layout and alter the positive and negative space. The layouts can be either symmetrical or asymetrical and this too will influence the shape placement. For symmetical spread, the folio structure is mirror to itself to produce a balanced layout. While for assymetrical, the folio structure repeat to produce a layout weighted to one side which is more dynamic.
(Week 5)
From the same book, I'm able to read about thinking in proportions which is one of the important aspects in design. The authors stated that the focal point of a design can vary in the piece and the proportions of the spatial relationships that it contains. The rule of thirds and the rule of odds are said to be the most effective ways of dealing with proportions.
Rude of thirds is a compositional guide used in design and photography to direct the positioning of key elements. Active 'hotsopots' will be created where the grid lines intersact when superimposing the basic three by three grid over a page. With these hotspots, the designer could place the key visual elements in it as to draw attention and give the design an offset balance that produces dynamic result. On the other hand, rule of odds is a compositional guide used in design and photography and places the subject of a design within an even number of surrounding objects. Thus, giving an odd number of total objects. As the result, the viewer will focus on the main subject while the supporting objects give balance to the design.





Comments
Post a Comment